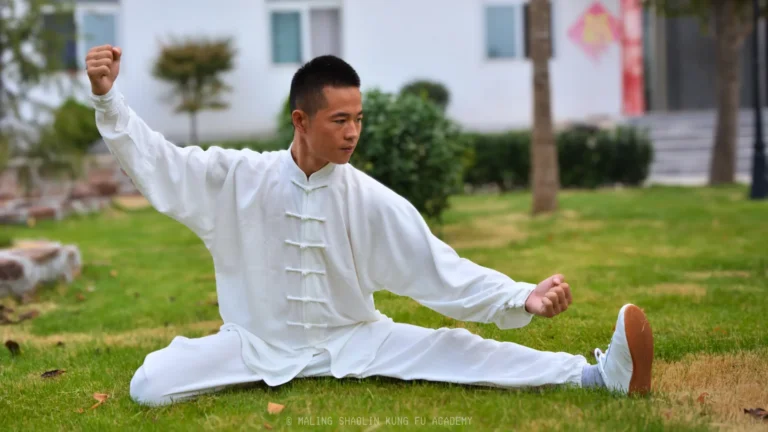
Image training, also known as visualization or mental rehearsal, is a practice where an individual uses their imagination to create or recreate experiences in their mind. This technique is widely used in various fields, including sports, martial arts, psychology, and professional development, to enhance performance and achieve specific goals.
How Image Training Works

1. Relaxation and Focus: Begin by finding a quiet place and assuming a comfortable position. Close your eyes and take a few deep breaths to relax your body and mind.
2. Creating Vivid Images: Visualize yourself performing a task or activity in great detail. This could be executing a martial arts move, giving a presentation, or completing a sports maneuver. The key is to make the mental image as vivid and detailed as possible.
3. Engaging All Senses: Try to engage all your senses in the visualization. Imagine the sights, sounds, smells, and physical sensations associated with the activity. This multi-sensory approach makes the experience more realistic and effective.
4. Positive Outcomes: Focus on successful outcomes. Visualize yourself performing the task flawlessly and achieving your goals. This helps build confidence and reduces anxiety related to the activity.
5. Repetition: Regularly practice image training. Just like physical practice, mental rehearsal benefits from consistent repetition, reinforcing neural pathways and improving muscle memory.
Benefits and Application in Martial Arts
Improved Technique and Precision: Image training allows martial artists to mentally rehearse their techniques, which can lead to improved precision and execution. By visualizing themselves performing a move correctly, they can reinforce the correct motor patterns in their brain, leading to better physical performance during actual practice.
Enhanced Mental Focus: Visualization helps in enhancing mental focus and concentration. Martial artists can use image training to visualize themselves in a state of deep concentration, blocking out distractions and maintaining focus on their movements and strategies. This mental discipline can translate to better focus during training and competitions.
Increased Confidence: Visualizing successful performance can boost confidence. When martial artists repeatedly imagine themselves executing techniques flawlessly, they build a sense of self-assurance. This increased confidence can help reduce anxiety and improve overall performance, especially in high-pressure situations.
Effective Strategy Development: Image training can be used to develop and refine strategies. Martial artists can visualize different scenarios and responses, allowing them to mentally prepare for various situations they might encounter. This mental rehearsal helps in developing quick decision-making skills and effective tactical responses.
Enhanced Muscle Memory: Repeated visualization of specific movements can enhance muscle memory. Martial artists who regularly practice image training can create strong neural pathways associated with their techniques. This can lead to faster and more efficient execution of moves during actual practice.
Practical Application: To incorporate image training, martial artists should find a quiet and comfortable place to sit or lie down. They should close their eyes and take a few deep breaths to relax. Then, they can start visualizing themselves performing specific techniques or sequences, paying attention to details such as posture, movement, and timing. It’s important to imagine the sensations and emotions associated with the practice to make the visualization more realistic.
Examples of Image Training in Media & Life
Kung Fu Movies
In many kung fu movies, characters often visualize battles or sequences of movements in their minds before engaging in a fight. Perhaps one of the most famous demonstrations of this is the mind battle between Jet Li and Donnie Yen in the classic 2002 movie “Hero.” These scenes depict the characters mentally rehearsing each move, anticipating their opponent’s actions, and planning their responses. This form of image training helps them prepare for the actual physical encounter, ensuring they are mentally and physically ready for the fight.
Sherlock Holmes’ Mind Palace
Sherlock Holmes, as portrayed in various films and television series, uses a technique called the “mind palace” or “memory palace.” This method involves creating a mental map of a familiar place and storing information within it. By visualizing this space and the information stored in it, Holmes can quickly retrieve and analyze details during his investigations. This form of image training enhances his cognitive abilities, allowing him to solve complex cases efficiently.
Athletic Visualization
Athletes across different sports use visualization techniques to improve their performance. For example, a gymnast might mentally rehearse their routine, visualizing each flip, twist, and landing with precision. This mental practice helps them perfect their movements and boosts their confidence, leading to better performance during actual competitions.
Martial Arts Taolu
In traditional martial arts, practitioners often visualize performing taolu or forms. They mentally go through each movement, focusing on the flow, technique, and timing. This practice helps them internalize the sequences, making their physical practice more effective and precise.
Public Speaking
Speakers often use image training to visualize themselves delivering their speech confidently. They imagine the audience’s positive reactions, their clear delivery, and their confident body language. This mental rehearsal reduces anxiety and helps them perform better during the actual speech.
Conclusion
Image training offers numerous benefits for martial artists, including improved technique, enhanced mental focus, increased confidence, effective strategy development, and enhanced muscle memory. By integrating visualization into their training regimen, martial artists can optimize both their physical and mental performance.





